Lecanosticta acicola(SCIRAC)
Photos
For publication in journals, books or magazines, permission should be obtained from the original photographers with a copy to EPPO.

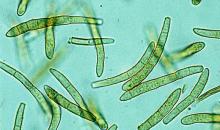
Lecanosticta conidia, to show variation in spore form with increasing altitude, on Pinus maximinoi (note decrease in size, septation, pigmentation and ornamentation with increasing altitude.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).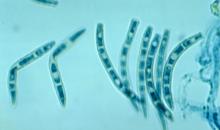
Lecanosticta conidia, to show variation in spore form with increasing altitude, on Pinus maximinoi (note decrease in size, septation, pigmentation and ornamentation with increasing altitude.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).
Brown to grey needles on Scotch pine (A) and stone pine (B) infected with brown-spot needle blight; conidial masses are protruding from both sides of the conidiomata under damp conditions (C) (bar 1 mm).
Courtesy: D Jurc, Forestry Institute, Ljubljana (SI).
A. Stromatic hyphae, conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and developing conidia in lactophenol-cotton blue (bar 20 µm) - B. conidia in water showing light brown colouration and verrucose structure (bar 50 µm) - C. in lactophenol-cotton blue showing septa and a thickened wall ( bar 20 µm).
Courtesy: D Jurc, Forestry Institute, Ljubljana (SI).
Lecanosticta anamorph of M. dearnessii; note solitary, discrete acervulus with green conidial cirrhus exuding onto needle.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).
Mycelium from an infected needle with olive green conidial masses after 15 days from isolation on malt extract agar (bar 5 mm).
Courtesy: D Jurc, Forestry Institute, Ljubljana (SI).
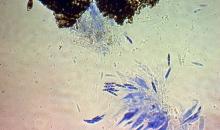
Slimy-dark green spore mass of Lecanosticta acicola produced from conidiomata under moist condition.

Lecanosticta acicola on Pinus oocarpa; note linearly arranged, solitary erumpent ascostromata.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).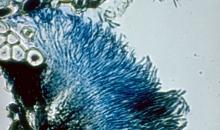
Acervulus (transverse section); note dark (green) spore mass.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).
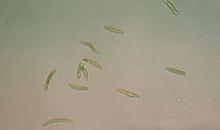
Dothistroma, conidia, from Pinus radiata; note hyaline, smooth, filiform, 1-3 septate spores.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).
Bbrown spot needle blight on second year foliage of Pinus maximinoi.
Courtesy: H.C. Evans, CABI, Wallingford (GB).