Monilinia fructicola(MONIFC)
Photos
All photos included on this page can only be used for educational purposes.
For publication in journals, books or magazines, permission should be obtained from the original photographers with a copy to EPPO.
For publication in journals, books or magazines, permission should be obtained from the original photographers with a copy to EPPO.

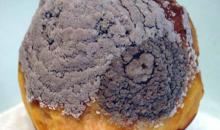
Symptoms caused by Monilinia fructicola- mummified peach fruit
Courtesy: Dmitrii Shukhin All-Russian Plant Quarantine Center
Lesions on apricot fruit due to M. fructicola, M. laxa & M. fructigena.Top left-control; top centre-M. laxa; top right-M. fructigena;bottom left-M. fructigena; bottom centre-M. fructicola; bottom right-M.laxa.
Courtesy: University of New South Wales (AU).
Lesions on pear fruit due to M. fructicola, M. laxa & M. fructigena. Top left-control; top centre-M. laxa; top right-M. fructigena; bottom left-M. fructigena; bottom centre-M. fructicola; bottom right-M.laxa.
Courtesy: H.J. Willetts, University of New South Wales (AU).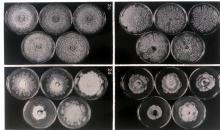
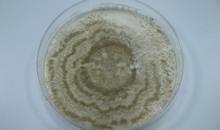
Cultural characteristics of Monilinia fructicola on PDA (2a) and V8 (2c) media in the dark at 25°C, compared with M. laxa (2b and d, respectively) -
Courtesy: University of New South Wales (AU).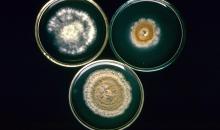
Colonies of M. fructigena (top left), M. laxa (top right), M. fructicola (bottom).
Courtesy: H.J. Willetts - University of New South Wales (AU).